-40%
TRAJAN DECIUS 249AD Viminacium Ancient Roman Coin BULL & LION LEGIONS i70783
$ 52.16
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Item:i70783
Authentic Ancient Coin of:
Trajan Decius
-
Roman Emperor
: 249-251 A.D.
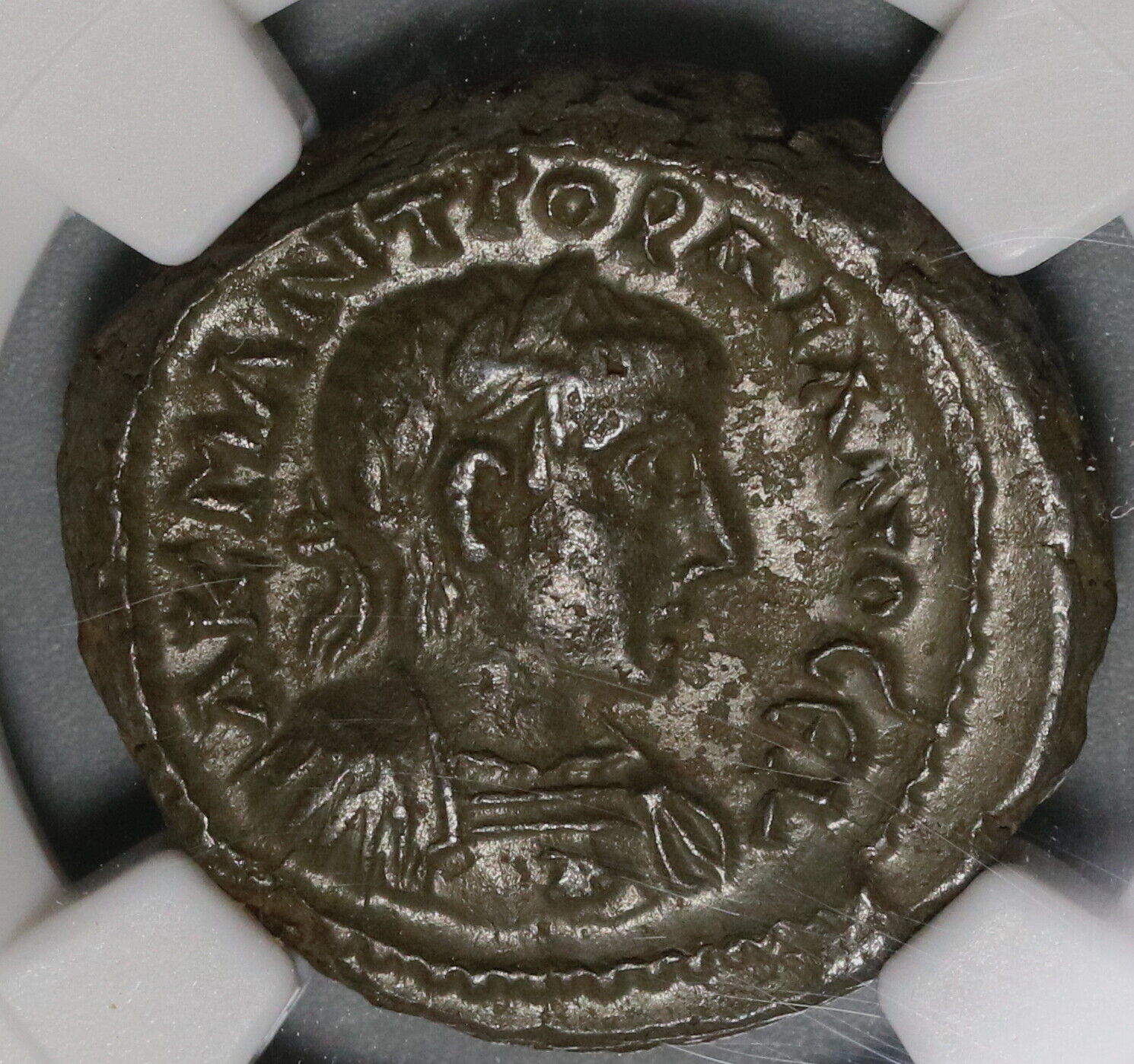
Bronze 21mm (5.17 grams) of Viminacium in Moesia Superior, dated Year 11,
struck 249/250 A.D.
Reference: Varbanov 163 corr.
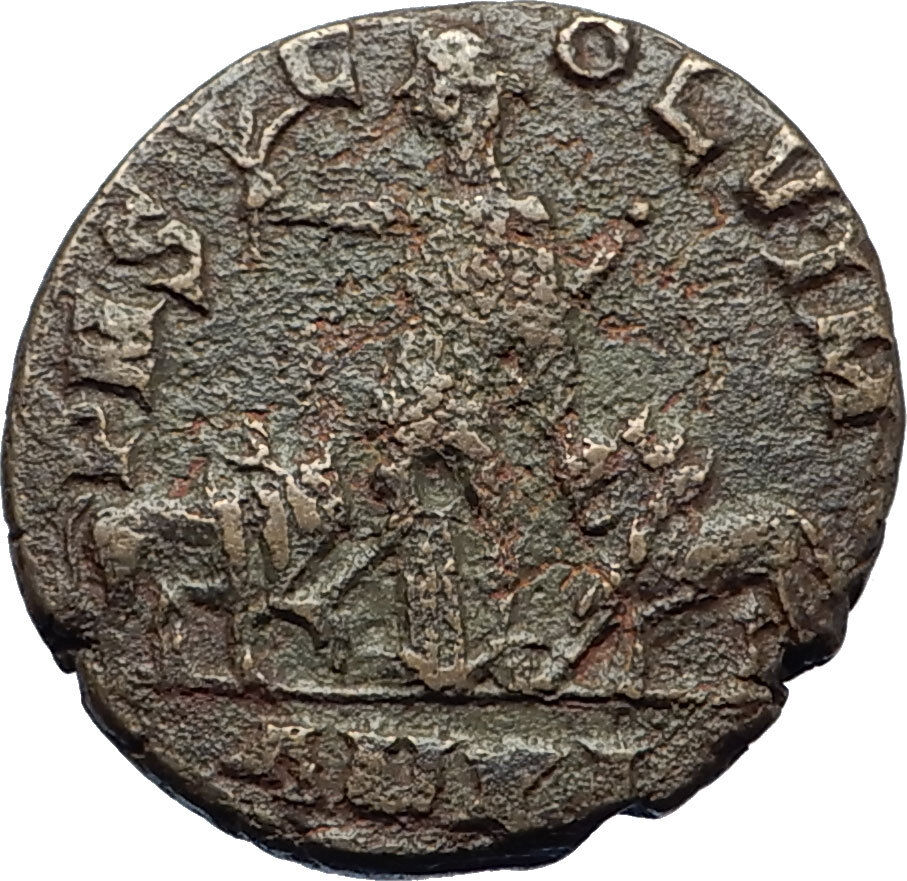
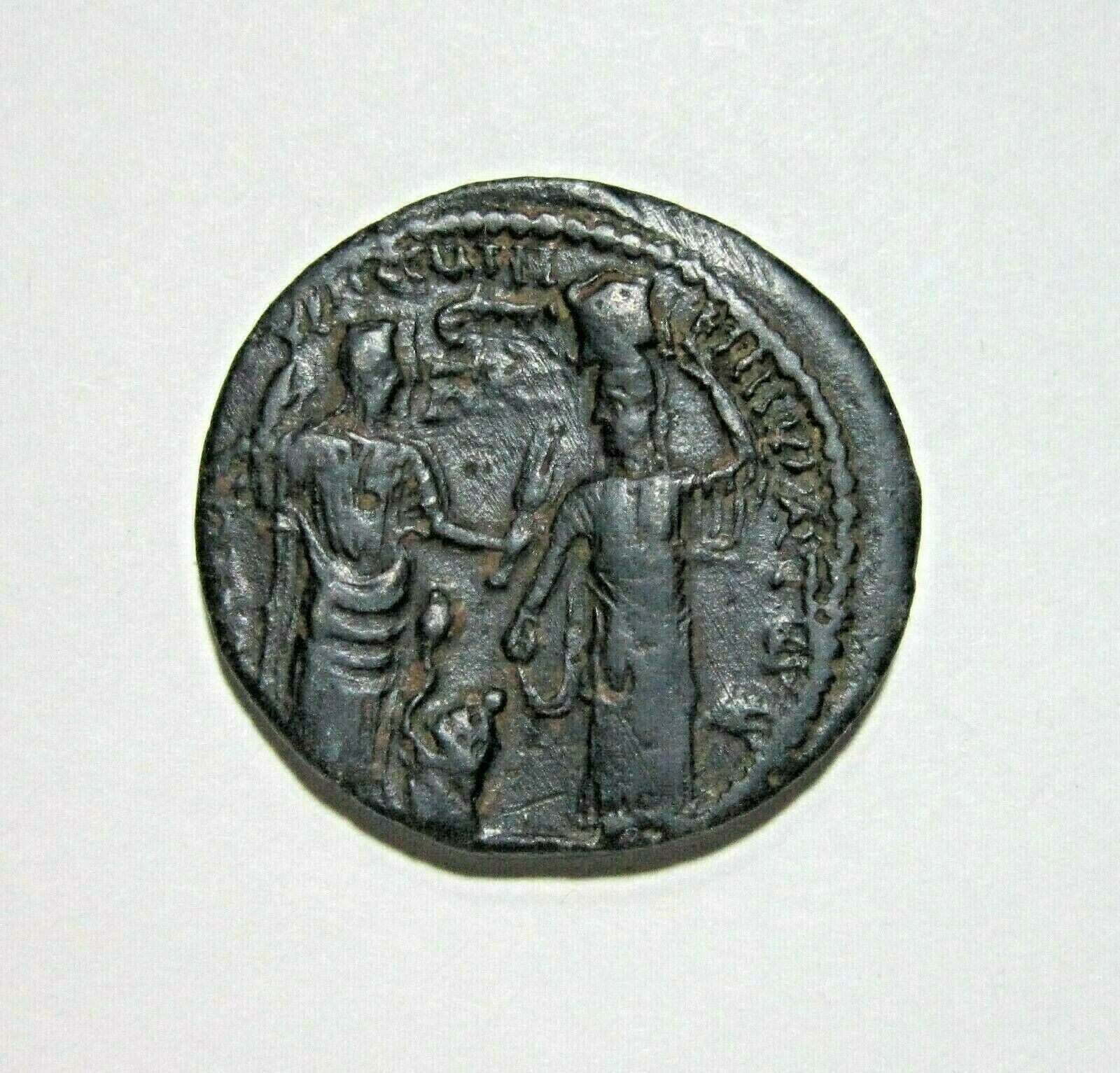
IMP TRAIANVS DECIVS AVG, Radiate, draped, and cuirassed right.
P M S COL VIM, Moesia-Pax standing facing, head left; to left, holding branch and transverse scepter with bull and lion standing on either side; AN XI (date) in exergue.
Viminacium was a major city of the Roman province of Moesia (today's Serbia), and the capital of Moesia Superior. Viminacium was the base camp of Legio VII Claudia, and hosted for some time the Legio IIII Flavia Felix. The bull and the lion depicted on the coins from the city were the symbols of the two legions. It was destroyed in 440 by the Huns.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Legio quarta Flavia Felix
("Lucky Flavian Fourth Legion"), was a legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in AD 70 by the emperor Vespasian (r. 69-79) from the ashes of the Legio IV
Macedonica
. The legion was active in Moesia Superior in the first half of the 5th century.
The legion symbol was a lion.
During the Batavian rebellion, the IV
Macedonica
fought for Vespasian, but the emperor distrusted his men, probably because they had supported Vitellius two years before. Therefore IV
Macedonica
was disbanded, and a new Fourth legion, called
Flavian Felix
was levied by the emperor, who gave the legio his nomen,
Flavia
. Since the symbol of the legion is a lion, it was probably levied in July/August 70.
IV
Flavia Felix
was camped in
Burnum
, Dalmatia (modern Kistanje), where it replaced XI
Claudia
. After the Dacian invasion of 86, Domitian moved the legion to Moesia Superior, in
Singidunum
(modern Belgrade, Serbia), although there is some evidence of the presence of this legion, of one of its
vexillationes
in
Viminacium
(near modern-day Kostolac, Serbia), base of VII
Claudia
.
In 88 the Fourth participated to the retaliation invasion of Dacia (see Domitian's Dacian War). It also participated in the Dacian Wars of Trajan, being victorious at the Second Battle of Tapae. The legion also participated at the final and decisive battle against the Dacians, conquering their capital, Sarmisegetusa.
Monuments of IV Flavia Felix have been found at Aquincum (Budapest). This suggests that a subunit replaced II Adiutrix during its absence during the wars of Lucius Verus against the Parthian empire (162-166).
In the Marcomannic Wars (166-180 AD), the fourth fought on the Danube against the Germanic tribes.
After the death of Pertinax, the IV
Flavia Felix
supported Septimius Severus against usurpers Pescennius Niger and Clodius Albinus.
The legion may have fought in one of the several wars against the Sassanids, but stayed in Moesia Superior until the first half of the 5th century.
This Roman Legion was featured in the beginning of the movie
Gladiator
where Maximus Decimus Meridius was the Legion general, leading the campaign in Germania against the Marcomanni.
Legio septima
Claudia Pia Fidelis
(
Seventh
Claudian
Legion
) was a Roman legion.
Its emblem, as well as of all Caesar's legions, was the bull
, together with the lion.
The 7th, along with the 6th, 8th & 9th were all founded by Pompey in Spain in 65 BC. They were ordered to Cisalpine Gaul around 58 BC by Julius Caesar, and marched with him throughout the entire Gallic Wars.
Legio VII was one of the two legions used in Caesar's invasions of Britain, and played a crucial role in The Battle of Pharsalus in 48 BC, and it existed at least until the end of the 4th century, guarding middle Danube.
Tiberius Claudius Maximus the Roman soldier who brought the head of Decebalus to emperor Trajan was serving in Legio VII Claudia.
Viminacium
(VIMINACIVM) was a major city (provincial capital) and military camp of the Roman province of Moesia (today's Serbia), and the capital of
Moesia Superior
. The site is located 12 km from the modern town of Kostolac in Eastern Serbia. The city dates back to the 1st century AD, and at its peak it is believed to have had 40.000 inhabitants, making it one of the biggest cities of that time. It lies on the Roman road
Via Militaris
. Viminacium was devastated by Huns in the 5th century, but was later rebuilt by Justinian. It was completely destroyed with the arrival of Slavs in the 6th century. Today, the archeological site occupies a total of 450 hectares, and contains remains of temples, streets, squares, amphitheatres, palaces, hippodromes and Roman baths.
History
The remains of Viminacium, the capital of the Roman province of Moesia Superior, are located on territories of the villages of Stari Kostolac and Drmno, about 12 km from the town of Kostolac and about 90 miles southeast of Belgrade. Viminacium was one of the most important Roman cities and military camps in the period from 1st to 4th centuries. Its exceptional strategic importance was reflected both in the defense of the northern border of the Roman empire and in turn of communications and commercial transactions. No less appealing to the Romans was the hinterland of the Mlava river valley, which is rich in ore and grains. In Roman times, the town on the northern side of relying directly on the branch of the Danube, while the western side, touching the walls Mlava rivers. Only in the later period, Viminacium spread to the left bank of Mlava. Thanks to the location, land and waterways, Viminacium represented one of those areas where the encounter of cultures between East and West was inevitable. Although these roads were the primary military and strategic function, they are taking place throughout antiquity very lively traffic and certainly contributed to the very Viminacium become prosperous and an important trading and business headquarters. In Viminacium, Roman legion VII Claudia was stationed, and a nearby civilian settlement emerged from the military camp. In 117 during the reign of Hadrian it received city status. In the camp, 6.000 soldiers were stationed, and 30-40.000 lived nearby. In the first half of the 3rd century the city was in full development, as evidenced by the fact that at that time it acquired the status of a Roman colony, and the right to coin local money. Here, in 211, Septimius Severus was proclaimed emperor by his son Caracalla. In the mausoleum and the excavated tombs, the Roman emperor Hostilian, who died in 251, was buried.
A legion may have been stationed here as early as Augustus (27 BC-14 AD). In 33/34 AD a road was built, linking Viminacium and Ratiaria. Claudius (41-54) garrisoned Viminacium, Oescus and Novae as camps for the Moesian legions.
The first legion attested at Viminacium was the VII Claudia that came from Dalmatia in 52 AD .
Emperor Trajan (98-117) was headquartered here during the Dacian Wars. It became a
colonia
with minting privilege in 239 AD during the rule of Gordian III (238-244) and housed the Legion VII and Legion IV.
Emperor Hostilian was the son of the emperor Decius, who was killed in the ambush near the ancient city of Abrutus located in present day Bulgaria. According to the old manuscript, emperor Hostilian and his mother came to Viminacium to supervise the organization of defense of northern borders, but both of them died of the plague. Because of the distance and the fear of spreading the plague, he was buried with all honors in Viminacium
Viminacium was the provincial capital of Moesia Superior. In the late spring of 293-294, Diocletian journeyed through his realm and he re-organized Viminacium as the capital of the new province of
Moesia Superior Margensis
. He registered that the people wrote in Latin, as opposed to Greek in the southern provinces. Viminacium was the base camp of Legio VII
Claudia
, and hosted for some time the IIII
Flavia Felix
. It had a Roman amphitheatre with room for 12,000 people.
In 382 the city was the meeting place between Theodosius and Gratian amidst the Gothic Wars.
Viminacium was destroyed in 441 by the Attila the Hun, but rebuilt by Justinian I. During Maurice's Balkan campaigns, Viminacium saw destruction by the Avars in 582 and a crushing defeat of Avar forces on the northern Danube bank in 599, destroying Avar reputation for invincibility.
Location and excavation
Viminacium is located in
Stari Kostolac
(Old
Kostolac
) a Serbian town on the Danube river, east of Belgrade. Viminacium is the location of the first archaeological excavation in Serbia, which started in 1882, by Mihailo Valtrović, an architect by profession and the first professor of archeology at the college in Belgrade. The only help he received was from 12 prisoners, because the state did not have enough resources to provide him with a better work force. His research was continued by Miloje Vasić, in the 1970s. It has intensified in the last ten years in the area of the Roman city of the Roman legionary camps and cemeteries. Many studies suggest that the military camp at Viminacium had a rectangular plan, measuring 442 x 385 meters, and that is not far from its western wall of civilian settlement in an area of approximately 72 acres. Legionary camp in Viminacium is now in a layer of arable land, so that wealth Viminacium easily accessible to researchers, but, unfortunately, and the robbers.The National Museum in Belgrade and Požarevac kept some 40,000 items found in Viminacium, of which over 700 made of gold and silver. Among them are many objects that represent the European and world rarities invaluable.
It has been discovered and more than 13,500 graves. Tombstones and sarcophagi are often decorated with relief representations of scenes from mythology or daily life. We have found numerous grave masonry construction. Especially interesting are the frescoes of the 4th-century tombs. Fresco with the notion of young women in artistic value of the extreme range of late antique art. During the excavation, an amphitheater, which with its 12,000 seats was one of the largest in the Balkans.
Gaius Messius Quintus Decius
(ca. 201- June 251) was the Emperor of Rome from 249 to 251. In the last year of his reign, he co-ruled with his son Herennius Etruscus until both of them were killed in the Battle of Abrittus.
Early life and rise to power
Decius, who was born at Budalia, now Martinci, Serbia near Sirmium (Sremska Mitrovica), in Lower Pannonia was one of the first among a long succession of future Roman Emperors to originate from the provinces of Illyria in the Danube.. Unlike some of his immediate imperial predecessors such as Philip the Arab or Maximinus, Decius was a distinguished senator who had served as consul in 232, had been governor of Moesia and Germania Inferior soon afterwards, served as governor of Hispania Tarraconensis between 235-238, and was urban prefect of Rome during the early reign of Emperor Philip the Arab (Marcus Iulius Phillipus).
Around 245, Emperor Philip entrusted Decius with an important command on the Danube. By the end of 248 or 249, Decius was sent to quell the revolt of Pacatianus and his troops in Moesia and Pannonia; the soldiers were enraged because of the peace treaty signed between Philip and the Sassanids. Once arrived, the troops forced Decius to assume the imperial dignity himself instead. Decius still protested his loyalty to Philip, but the latter advanced against him and was killed near Verona, Italy. The Senate then recognized Decius as Emperor, giving him the attribute
Traianus
as a reference to the good emperor Trajan. As the Byzantine historian Zosimus later noted:
Decius was therefore clothed in purple and forced to undertake the [burdens of] government, despite his reluctance and unwillingness.
Political and monumental initiatives
Decius' political program was focused on the restoration of the strength of the State, both military opposing the external threats, and restoring the public piety with a program of renovation of the State religion.
Either as a concession to the Senate, or perhaps with the idea of improving public morality, Decius endeavoured to revive the separate office and authority of the censor. The choice was left to the Senate, who unanimously selected Valerian (afterwards emperor). But Valerian, well aware of the dangers and difficulties attaching to the office at such a time, declined the responsibility. The invasion of the Goths and Decius' death put an end to the abortive attempt.
During his reign, he proceeded to construct several building projects in Rome "including the Thermae Deciane or Baths of Decius on the Aventine" which was completed in 252 and still survived through to the 16th century; Decius also acted to repair the Colosseum, which had been damaged by lightning strikes.
Persecution of Christians
In January 250, Decius issued an edict for the suppression of Christianity. The edict itself was fairly clear:
All the inhabitants of the empire were required to sacrifice before the magistrates of their community 'for the safety of the empire' by a certain day (the date would vary from place to place and the order may have been that the sacrifice had to be completed within a specified period after a community received the edict). When they sacrificed they would obtain a certificate (libellus) recording the fact that they had complied with the order.
While Decius himself may have intended the edict as a way to reaffirm his conservative vision of the Pax Romana and to reassure Rome's citizens that the empire was still secure, it nevertheless sparked a "terrible crisis of authority as various [Christian] bishops and their flocks reacted to it in different ways." Measures were first taken demanding that the bishops and officers of the church make a sacrifice for the Emperor, a matter of an oath of allegiance that Christians considered offensive. Certificates were issued to those who satisfied the pagan commissioners during the persecution of Christians under Decius. Forty-six such certificates have been published, all dating from 250, four of them from Oxyrhynchus. Christian followers who refused to offer a pagan sacrifice for the Emperor and the Empire's well-being by a specified date risked torture and execution. A number of prominent Christians did, in fact, refuse to make a sacrifice and were killed in the process including Pope Fabian himself in 250 and "anti-Christian feeling[s] led to pogroms at Carthage and Alexandria." In reality, however, towards the end of the second year of Decius' reign, "the ferocity of the [anti-Christian] persecution had eased off, and the earlier tradition of tolerance had begun to reassert itself." The Christian church though never forgot the reign of Decius whom they labelled as that "fierce tyrant".
At this time, there was a second outbreak of the Antonine Plague, which at its height in 251 to 266 took the lives of 5,000 a day in Rome. This outbreak is referred to as the "Plague of Cyprian" (the bishop of Carthage), where both the plague and the persecution of Christians were especially severe. Cyprian's biographer Pontius gave a vivid picture of the demoralizing effects of the plague and Cyprian moralized the event in his essay
De mortalitate
. In Carthage the "Decian persecution" unleashed at the onset of the plague sought out Christian scapegoats. Decius' edicts were renewed under Valerius in 253 and repealed under his son, Gallienus, in 260-1.
Military actions and death
The barbarian incursions into the Empire were becoming more and more daring and frequent whereas the Empire was facing a serious economic crisis in Decius' time. During his brief reign, Decius engaged in important operations against the Goths, who crossed the Danube to raid districts of Moesia and Thrace. This is the first considerable occasion the Goths �" who would later come to play such an important role �" appear in the historical record. The Goths under King Cniva were surprised by the emperor while besieging Nicopolis on the Danube; the Goths fled through the difficult terrain of the Balkans, but then doubled back and surprised the Romans near Beroë (modern Stara Zagora), sacking their camp and dispersing the Roman troops. It was the first time a Roman emperor fled in the face of Barbarians. The Goths then moved to attack
Philippopolis
(modern Plovdiv), which fell into their hands. The governor of Thrace, Titus Julius Priscus, declared himself Emperor under Gothic protection in opposition to Decius but Priscus's challenge was rendered moot when he was killed soon afterwards.
The siege of Philippopolis had so exhausted the numbers and resources of the Goths that they offered to surrender their treasure and prisoners, on condition of being allowed to retire.
[
citation needed
]
Decius, who had succeeded in surrounding them and hoped to cut off their retreat, refused to entertain their proposals. The final engagement, in which the Goths fought with the courage of despair, under the command of Cniva, took place during the second week of June 251 on swampy ground in the Ludogorie (region in northeastern Bulgaria which merges with Dobruja plateau and the Danube Plain to the north) near the small settlement of Abrittus or
Forum Terebronii
(modern Razgrad): see Battle of Abrittus. Jordanes records that Decius' son Herennius Etruscus was killed by an arrow early in the battle, and to cheer his men Decius exclaimed, "Let no one mourn; the death of one soldier is not a great loss to the republic." Nevertheless, Decius' army was entangled in the swamp and annihilated in this battle, while he himself was killed on the field of battle. As the historian Aurelius Victor relates:
The Decii (ie.
Decius
), while pursuing the barbarians across the Danube, died through treachery at Abrittus after reigning two years....Very many report that the son had fallen in battle while pressing an attack too boldly; that the father however, has strenuously asserted that the loss of one soldier seemed to him too little to matter. And so he resumed the war and died in a similar manner while fighting vigorously.
One literary tradition claims that Decius was betrayed by his successor Trebonianus Gallus, who was involved in a secret alliance with the Goths but this cannot be substantiated and was most likely a later invention since Gallus felt compelled to adopt Decius' younger son, Gaius Valens Hostilianus, as joint emperor even though the latter was too young to rule in his own right. It is also unlikely that the shattered Roman legions would proclaim as emperor a traitor who was responsible for the loss of so many soldiers from their ranks. Decius was the first Roman emperor to die in battle against a foreign enemy
Frequently Asked Questions
Mr. Ilya Zlobin
, world-renowned expert numismatist, enthusiast, author and dealer in authentic ancient Greek, ancient Roman, ancient Byzantine, world coins & more.
Who am I dealing with?
You are dealing with Ilya Zlobin, ancient coin expert, enthusiast, author and dealer with an online store having a selection of over 15,000 items with great positive feedback from verified buyers and over 10 years experience dealing with over 57,000 ancient and world coins and artifacts. Ilya Zlobin is an independent individual who has a passion for coin collecting, research and understanding the importance of the historical context and significance all coins and objects represent. Most others are only concerned with selling you, Ilya Zlobin is most interested in educating you on the subject, and providing the largest selection, most professional presentation and service for the best long-term value for collectors worldwide creating returning patrons sharing in the passion of ancient and world coin collecting for a lifetime.
How long until my order is shipped?
Orders are shipped by the next business day (after receipt of payment) most of the time.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date could be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date. Any tracking number would be found under your 'Purchase history' tab.
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S. International shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country.
Standard international mail to many countries
does not
include a tracking number, and can also be slow sometimes.
For a tracking number and signature confirmation, you may want to do Express Mail International Shipping, which costs more, however, is the fastest and most secure. Additionally you may be able to receive your order in as little as 3-5 business days using this method. For Express Mail International, it may be possible to place up to 10-15 items in one package (for the one shipping cost) as it is flat rate envelope, which may be the most cost-effective, secure and fastest way to receive items internationally. Send me a message about this and I can update your invoice should you want this method.
Getting your order to you, quickly and securely is a top priority and is taken seriously here.
Great care is taken in packaging and mailing every item securely and quickly.
Please be aware, I cannot take responsibility for any postal service delivery delays, especially for international packages as it may happen in rare instances.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 57,000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be very happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing. Additionally, the coin is inside it's own protective coin flip (holder), with a 2x2 inch description of the coin matching the individual number on the COA.
On the free-market such a presentation alone, can be considered a - value all in itself, and it comes standard with your purchases from me,
FREE.
With every purchase, you are leveraging my many years of experience to get a more complete context and understanding of the piece of history you are getting. Whether your goal is to collect or give the item as a gift, coins presented like this could be more prized and valued higher than items that were not given such care and attention to.
Buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive feedback. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens sometimes that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for their order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.
How and where do I learn more about collecting ancient coins?
Visit the "
Guide on How to Use My Store
" for on an overview about using my store, with additional information and links to all other parts of my store which may include educational information on topics you are looking for.