-40%
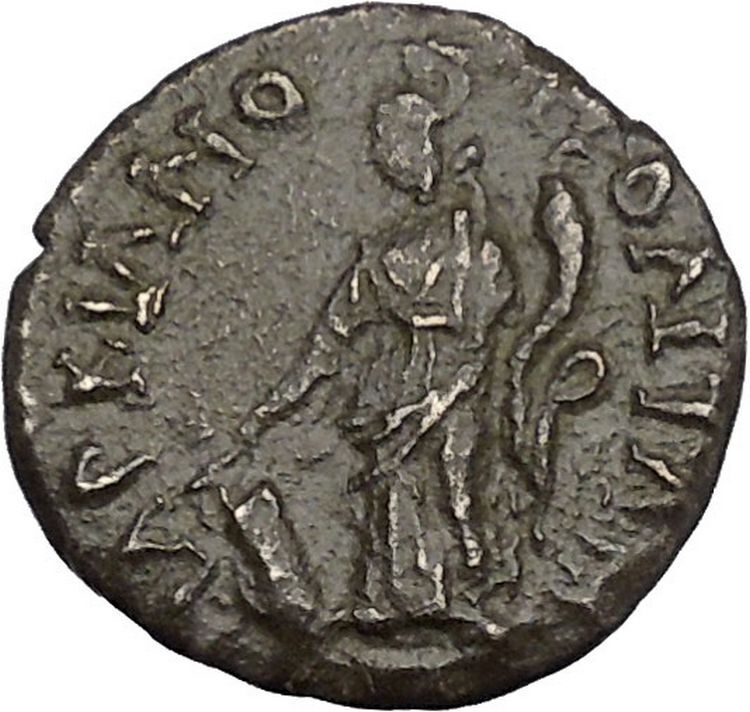
SEPTIMIUS SEVERUS Marcianopolis Moesia Ancient Roman Coin Fortuna Tyche i47929
$ 36.96
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
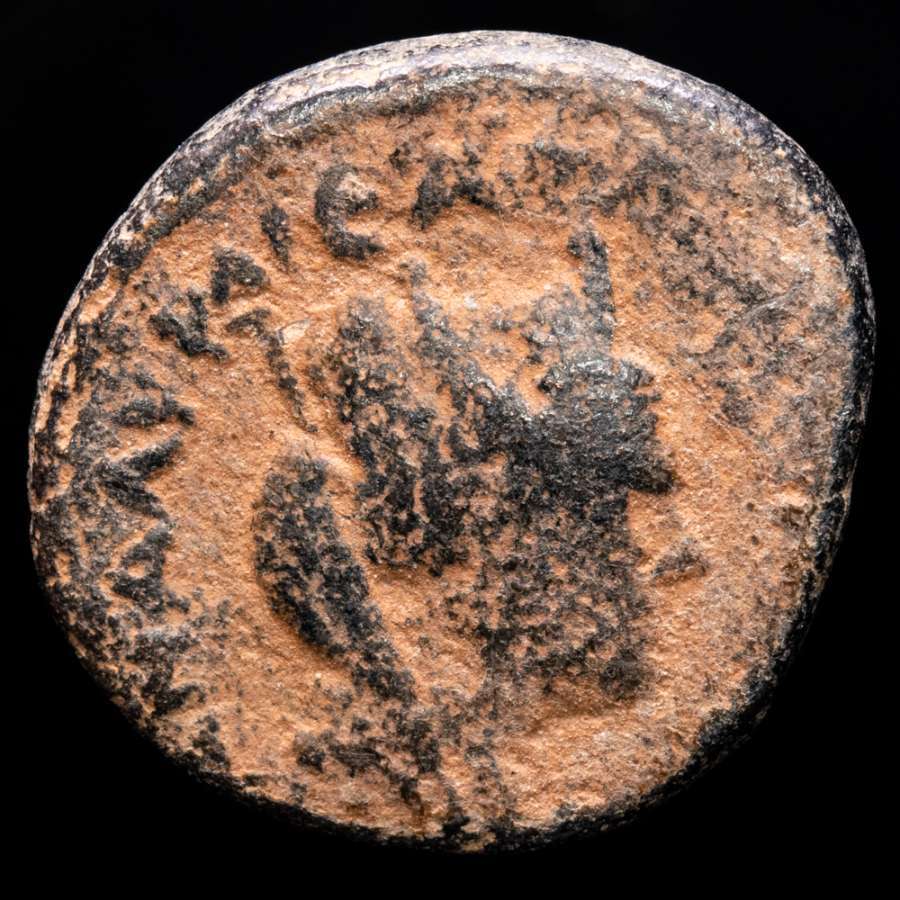
Item:i47929
Authentic Ancient Coin of:
Septimius Severus
-
Roman Emperor
: 193-211 A.D. -
Bronze 19mm (4.11 grams)
<="" font="" color="#000000" face="Times New Roman">of
Marcianopolis
in Moesia Inferior
AV KAI C
Є
C
Є
VHPO, Laureate, draped and cuirassed bust right.
MAPKIANOΠOΛITΩN,
Tyche
standing left, holding rudder and cornucopia.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
The
cornucopia
(from Latin
cornu copiae
) or
horn of plenty
is a symbol of abundance and nourishment, commonly a large horn-shaped container overflowing with produce, flowers, nuts, other edibles, or wealth in some form. Originating in
classical antiquity
, it has continued as a symbol in
Western art
, and it is particularly associated with the
Thanksgiving
holiday in
North America
.
Allegorical
depiction of the Roman goddess
Abundantia
with a cornucopia, by
Rubens
(
ca.
1630)
In Mythology
Mythology
offers multiple
explanations of the origin
of the cornucopia. One of the best-known involves the birth and nurturance of the infant
Zeus
, who had to be hidden from his devouring father
Cronus
. In a cave on
Mount Ida
on the island of
Crete
, baby Zeus was cared for and protected by a number of divine attendants, including the goat
Amalthea
("Nourishing Goddess"), who fed him with her milk. The suckling future king of the gods had unusual abilities and strength, and in playing with his nursemaid accidentally broke off one of her
horns
, which then had the divine power to provide unending nourishment, as the foster mother had to the god.
In another myth, the cornucopia was created when
Heracles
(Roman
Hercules
) wrestled with the river god
Achelous
and wrenched off one of his horns; river gods were sometimes depicted as horned. This version is represented in the
Achelous and Hercules
mural painting
by the
American Regionalist
artist
Thomas Hart Benton
.
The cornucopia became the attribute of several
Greek
and
Roman deities
, particularly those associated with the harvest, prosperity, or spiritual abundance, such as personifications of Earth (
Gaia
or
Terra
); the child
Plutus
, god of riches and son of the grain goddess
Demeter
; the
nymph
Maia
; and
Fortuna
, the goddess of luck, who had the power to grant prosperity. In
Roman Imperial cult
, abstract Roman deities who fostered peace
(
pax Romana
)
and prosperity were also depicted with a cornucopia, including
Abundantia
, "Abundance" personified, and
Annona
, goddess of the
grain supply to the city of Rome
.
Pluto
, the classical ruler of the underworld in the
mystery religions
, was a giver of agricultural, mineral and spiritual wealth, and in art often holds a cornucopia to distinguish him from the gloomier
Hades
, who holds a
drinking horn
instead.
Modern depictions
In modern depictions, the cornucopia is typically a hollow, horn-shaped wicker basket filled with various kinds of festive
fruit
and
vegetables
. In North America, the cornucopia has come to be associated with
Thanksgiving
and the harvest. Cornucopia is also the name of the annual November Wine and Food celebration in
Whistler
, British Columbia, Canada. Two cornucopias are seen in the
flag
and
state seal
of
Idaho
. The Great
Seal
of
North Carolina
depicts Liberty standing and Plenty holding a cornucopia. The coat of arms of
Colombia
,
Panama
,
Peru
and
Venezuela
, and the Coat of Arms of the State of
Victoria, Australia
, also feature the cornucopia, symbolising prosperity.
The horn of plenty is used on body art and at Halloween, as it is a symbol of fertility, fortune and abundance.
Base of a statue of
Louis XV of France
Tyche (Greek for luck; the Roman equivalent was
Fortuna
) was the presiding
tutelary deity
that governed the fortune and prosperity of a city, its destiny. Increasingly during the Hellenistic period, cities had their own specific iconic version of Tyche, wearing a
mural crown
(a crown like the walls of the city).
The Greek historian
Polybius
believed that when no cause can be discovered to events such as floods, droughts, frosts or even in politics, then the cause of these events may be fairly attributed to Tyche.
Stylianos Spyridakis concisely expressed Tyche's appeal in a Hellenistic world of arbitrary violence and unmeaning reverses: "In the turbulent years of the
Epigoni of Alexander
, an awareness of the instability of human affairs led people to believe that Tyche, the blind mistress of Fortune, governed mankind with an inconstancy which explained the vicissitudes of the time."
In literature, she might be given various genealogies, as a daughter of
Hermes
and
Aphrodite
, or considered as one of the
Oceanids
, daughters of
Oceanus
and
Tethys
, or of
Zeus
. She was connected with
Nemesis
and
Agathos Daimon
("good spirit").
She was uniquely venerated at
Itanos
in Crete, as
Tyche Protogeneia
, linked with the Athenian
Protogeneia
("firstborn"), daughter of
Erechtheus
, whose self-sacrifice saved the city.
She had temples at
Caesarea Maritima
,
Antioch
,
Alexandria
and
Constantinople
. In
Alexandria
the
Tychaeon
, the temple of Tyche, was described by
Libanius
as one of the most magnificent of the entire Hellenistic world.
Tyche appears on many
coins
of the Hellenistic period in the three centuries before the Christian era, especially from cities in the Aegean. Unpredictable turns of fortune drive the complicated plotlines of
Hellenistic romances
, such as
Leucippe and Clitophon
or
Daphnis and Chloe
. She experienced a resurgence in another era of uneasy change, the final days of publicly sanctioned
Paganism
, between the late-fourth-century emperors
Julian
and
Theodosius I
who definitively closed the temples. The effectiveness of her capricious power even achieved respectability in philosophical circles during that generation, though among poets it was a commonplace to revile her for a fickle harlot.
In
medieval art
, she was depicted as carrying a
cornucopia
, an
emblematic
ship's rudder, and the
wheel of fortune
, or she may stand on the wheel, presiding over the entire circle of fate.
The constellation of
Virgo
is sometimes identified as the heavenly figure of Tyche, as well as other goddesses such as
Demeter
and
Astraea
.
Marcianopolis
, or
Marcianople
was an ancient Roman city in
Thracia
. It was located at the site of modern day
Devnya
,
Bulgaria
.
The city was so renamed by Emperor
Trajan
after his sister
Ulpia Marciana
, and was previously known as Parthenopolis. Romans repulsed a
Gothic
attack to this town in
267
(or
268
), during the reign of
Gallienus
.
Diocletian
made it the capital of the
Moesia Secunda
province.
Valens
made it his winter quarters in 368 and succeeding years, Emperor
Justinian I
restored and fortified it. In 587, it was sacked by the king of the
Avars
but at once retaken by the Romans. The Roman army quartered there in 596 before crossing the Danube to assault the Avars.
Between 893 and 972 it was one of the most important medieval cities in south-eastern Europe.
L
ucius Septimius Severus
(or rarely
Severus I
) (April 11, 145/146-February 4, 211) was a
Roman
general, and
Roman Emperor
from April 14, 193 to 211. He was born in what is now the
Berber
part of Rome's historic
Africa Province
.
Septimius Severus was born and raised at
Leptis Magna
(modern
Berber
, southeast of
Carthage
, modern
Tunisia
). Severus came from a wealthy, distinguished family of
equestrian
rank. Severus was of
Italian
Roman ancestry on his mother's side and of
Punic
or
Libyan
-Punic ancestry on his father's. Little is known of his father,
Publius Septimius Geta
, who held no major political status but had two cousins who served as consuls under emperor
Antoninus Pius
. His mother, Fulvia Pia's family moved from
Italy
to
North Africa
and was of the
Fulvius
gens, an ancient and politically influential clan, which was originally of
plebeian
status. His siblings were a younger
Publius Septimius Geta
and Septimia Octavilla. Severus’s maternal cousin was
Praetorian Guard
and consul
Gaius Fulvius Plautianus
.
In 172, Severus was made a
Senator
by the then emperor
Marcus Aurelius
. In 187 he married secondly
Julia Domna
. In 190 Severus became
consul
, and in the following year received from the emperor
Commodus
(successor to Marcus Aurelius) the command of the
legions
in
Pannonia
.
On the murder of
Pertinax
by the troops in 193, they proclaimed Severus Emperor at
Carnuntum
, whereupon he hurried to Italy. The former emperor,
Didius Julianus
, was condemned to death by the Senate and killed, and Severus took possession of Rome without opposition.
The legions of
Syria
, however, had proclaimed
Pescennius Niger
emperor. At the same time, Severus felt it was reasonable to offer
Clodius Albinus
, the powerful governor of Britannia who had probably supported Didius against him, the rank of Caesar, which implied some claim to succession. With his rearguard safe, he moved to the East and crushed Niger's forces at the
Battle of Issus
. The following year was devoted to suppressing Mesopotamia and other Parthian vassals who had backed Niger. When afterwards Severus declared openly his son
Caracalla
as successor, Albinus was hailed emperor by his troops and moved to Gallia. Severus, after a short stay in Rome, moved northwards to meet him. On
February 19
,
197
, in the
Battle of Lugdunum
, with an army of 100,000 men, mostly composed of
Illyrian
,
Moesian
and
Dacian
legions, Severus defeated and killed Clodius Albinus, securing his full control over the Empire.
Emperor
Severus was at heart a
soldier
, and sought glory through military exploits. In 197 he waged a brief and successful war against the
Parthian Empire
in retaliation for the support given to Pescennius Niger. The Parthian capital
Ctesiphon
was sacked by the legions, and the northern half of
Mesopotamia
was restored to Rome.
His relations with the
Roman Senate
were never good. He was unpopular with them from the outset, having seized power with the help of the military, and he returned the sentiment. Severus ordered the execution of dozens of Senators on charges of corruption and
conspiracy
against him, replacing them with his own favorites.
He also disbanded the
Praetorian Guard
and replaced it with one of his own, made up of 50,000 loyal soldiers mainly camped at
Albanum
, near Rome (also probably to grant the emperor a kind of centralized reserve). During his reign the number of legions was also increased from 25/30 to 33. He also increased the number of auxiliary corps (
numerii
), many of these troops coming from the Eastern borders. Additionally the annual wage for a soldier was raised from 300 to 500
denarii
.
Although his actions turned Rome into a military
dictatorship
, he was popular with the citizens of Rome, having stamped out the rampant corruption of Commodus's reign. When he returned from his victory over the Parthians, he erected the
Arch of Septimius Severus
in Rome.
According to Cassius Dio, however, after 197 Severus fell heavily under the influence of his Praetorian Prefect,
Gaius Fulvius Plautianus
, who came to have almost total control of most branches of the imperial administration. Plautianus's daughter,
Fulvia Plautilla
, was married to Severus's son, Caracalla. Plautianus’s excessive power came to an end in 205, when he was denounced by the Emperor's dying brother and killed. The two following
praefecti
, including the jurist
Aemilius Papinianus
, received however even larger powers.
Campaigns in Caledonia (Scotland)
Starting from 208 Severus undertook a number of military actions in
Roman Britain
, reconstructing
Hadrian's Wall
and campaigning in
Scotland
.
He reached the area of the
Moray Firth
in his last campaign in Caledonia, as was called Scotland by the Romans.. In 210 obtained a peace with the
Picts
that lasted practically until the final withdrawal of the Roman legions from Britain, before falling severely ill in
Eboracum
(
York
).
Death
He is famously said to have given the advice to his sons: "Be harmonious, enrich the soldiers, and scorn all other men" before he died at Eboracum on
February 4
,
211
. Upon his death in 211, Severus was
deified
by the Senate and succeeded by his sons,
Caracalla
and
Geta
, who were advised by his wife
Julia Domna
. The stability Severus provided the Empire was soon gone under their reign.
Accomplishments and Record
Though his military expenditure was costly to the empire, Severus was the strong, able ruler that Rome needed at the time. He began a tradition of effective emperors elevated solely by the military. His policy of an expanded and better-rewarded army was criticized by his contemporary
Dio Cassius
and
Herodianus
: in particular, they pointed out the increasing burden (in the form of taxes and services) the civilian population had to bear to maintain the new army.
Severus was also distinguished for his buildings. Apart from the triumphal arch in the Roman Forum carrying his full name, he also built the
Septizodium
in Rome and enriched greatly his native city of
Leptis Magna
(including another triumphal arch on the occasion of his visit of 203).
Severus and Christianity
Christians were
persecuted
during the reign of Septimus Severus. Severus allowed the enforcement of policies already long-established, which meant that Roman authorities did not intentionally seek out Christians, but when people were accused of being Christians they could either curse
Jesus
and make an offering to
Roman gods
, or be executed. Furthermore, wishing to strengthen the peace by encouraging religious harmony through
syncretism
, Severus tried to limit the spread of the two quarrelsome groups who refused to yield to syncretism by outlawing
conversion
to Christianity or
Judaism
. Individual officials availed themselves of the laws to proceed with rigor against the Christians. Naturally the emperor, with his strict conception of law, did not hinder such partial persecution, which took place in
Egypt
and the
Thebaid
, as well as in
Africa proconsularis
and the East. Christian
martyrs
were numerous in
Alexandria
(cf.
Clement of Alexandria
,
Stromata
, ii. 20;
Eusebius
,
Church History
, V., xxvi., VI., i.). No less severe were the persecutions in Africa, which seem to have begun in 197 or 198 (cf.
Tertullian's
Ad martyres
), and included the Christians known in the
Roman martyrology
as the martyrs of
Madaura
. Probably in 202 or 203
Felicitas
and
Perpetua
suffered for their faith. Persecution again raged for a short time under the proconsul
Scapula
in 211, especially in
Numidia
and
Mauritania
. Later accounts of a
Gallic
persecution, especially at
Lyon
, are legendary. In general it may thus be said that the position of the Christians under Septimius Severus was the same as under the
Antonines
; but the law of this Emperor at least shows clearly that the
rescript
of
Trajan
[
clarification needed
]
had failed to execute its purpose.
="">
Frequently Asked Questions
How long until my order is shipped?
Depending on the volume of sales, it may take up to 5 business days for shipment of your order after the receipt of payment.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date should be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date.
After you shipped the order, how long will the mail take?
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S., international shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country. I am not responsible for any USPS delivery delays, especially for an international package.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 10000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be quite happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing.
Compared to other certification companies, the certificate of authenticity is a -50 value. So buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
Is there a number I can call you with questions about my order?
You can contact me directly via ask seller a question and request my telephone number, or go to my About Me Page to get my contact information only in regards to items purchased on eBay.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens many times that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for the order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.