-40%
ELAGABALUS & JULIA MAESA Ancient Marcianopolis Roman Coin w DIONYSUS i79974
$ 52.16
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Item:i79974
Authentic Ancient Coin of:
Elagabalus
-
Roman Emperor
: 218-222 A.D.
Elagabalus and Julia Maesa
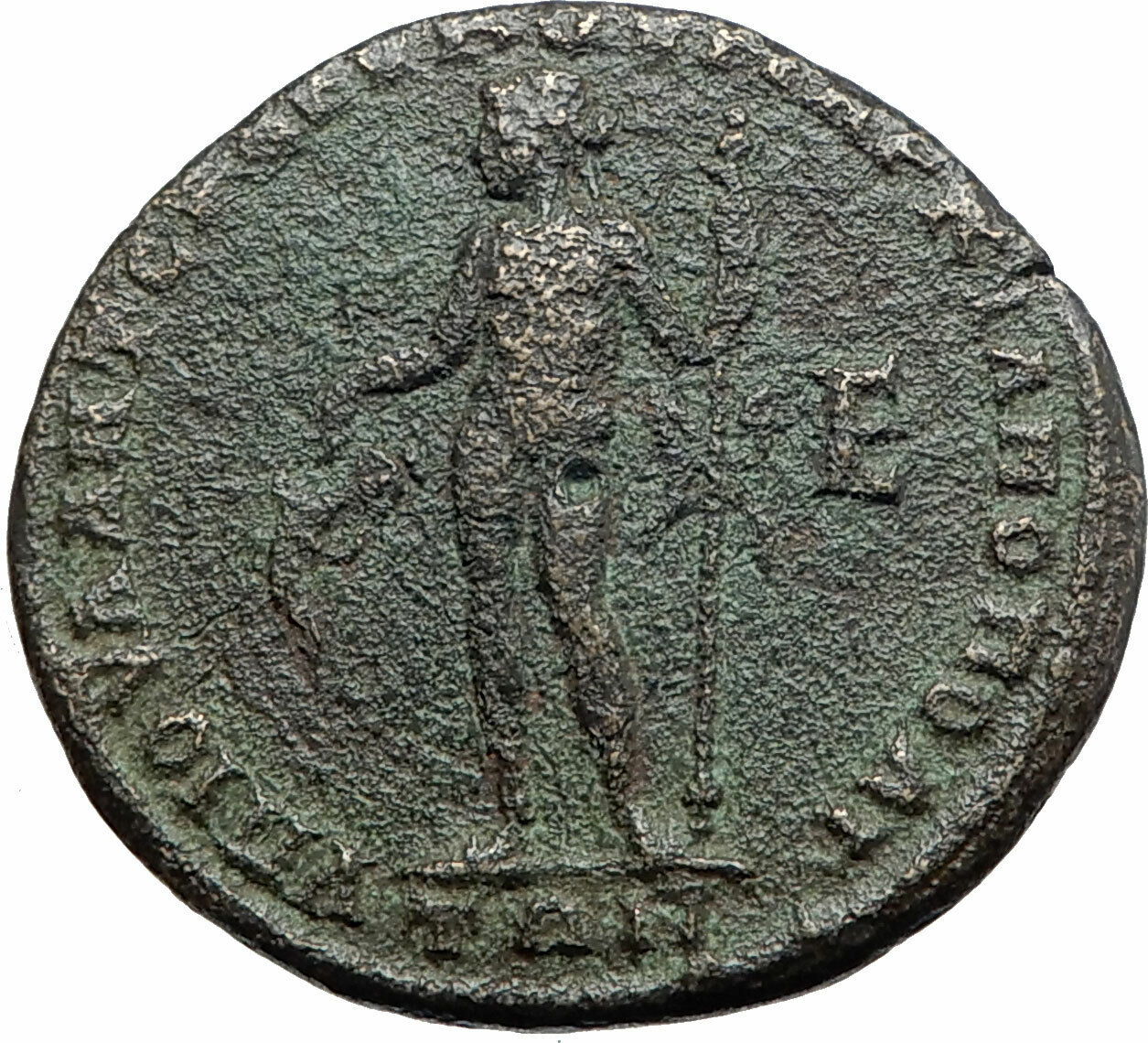
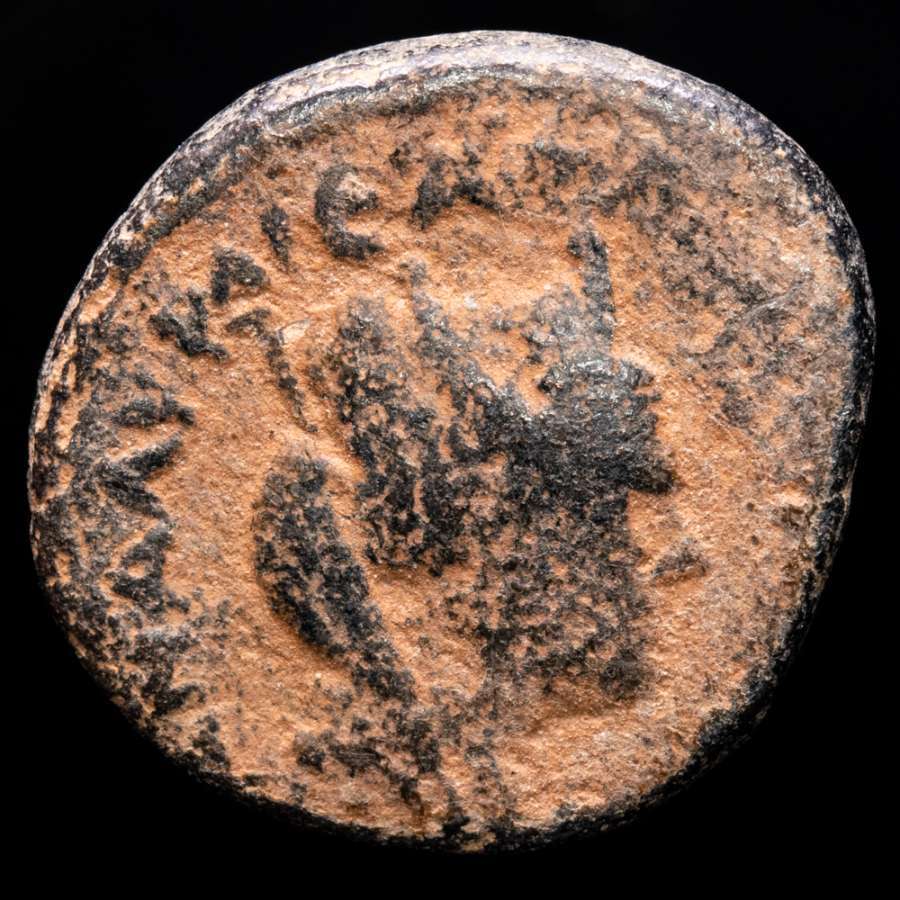
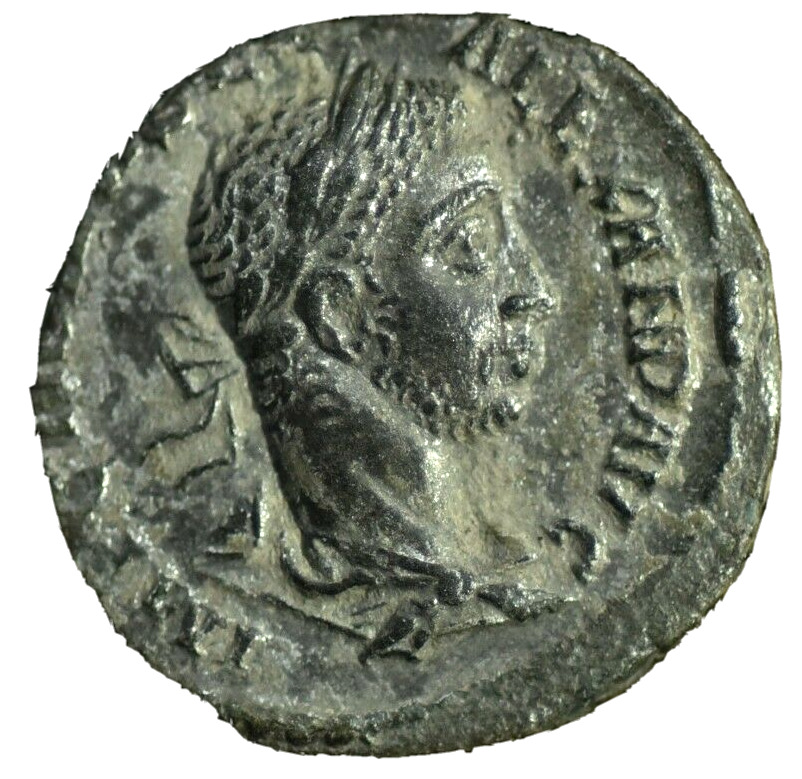
Bronze 'Pentassarion' 25mm (8.17 grams) of
Marcianopolis
in Moesia Inferior under Magistrate Seleucus.
Laureate draped bust of Elagabalus and diademed draped bust of Julia Maesa facing each other.
VΠ IOVΛ ANT CEΛEVKOV MAPKIANOΠOΛITΩN, Nude Dionysus standing facing, his head head left, holding kantharos from which he pours out wine and holding a thyrsost; E (value mark) in field to right.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Dionysus
is the god of the grape harvest, winemaking and wine, of ritual madness, fertility, theatre and religious ecstasy in Greek mythology. Alcohol, especially wine, played an important role in Greek culture with Dionysus being an important reason for this life style. His name, thought to be a theonym in Linear B tablets as
di-wo-nu-so
(KH Gq 5 inscription), shows that he may have been worshipped as early as c. 1500-1100 BC by Mycenean Greeks; other traces of the Dionysian-type cult have been found in ancient Minoan Crete. His origins are uncertain, and his cults took many forms; some are described by ancient sources as Thracian, others as Greek. In some cults, he arrives from the east, as an Asiatic foreigner; in others, from Ethiopia in the South. He is a god of epiphany, "the god that comes", and his "foreignness" as an arriving outsider-god may be inherent and essential to his cults. He is a major, popular figure of Greek mythology and religion, and is included in some lists of the twelve Olympians. Dionysus was the last god to be accepted into Mt. Olympus. He was the youngest and the only one to have a mortal mother. His festivals were the driving force behind the development of Greek theatre. Modern scholarship categorises him as a dying-and-rising god.
The earliest cult images of Dionysus show a mature male, bearded and robed. He holds a fennel staff, tipped with a pine-cone and known as a
thyrsus
. Later images show him as a beardless, sensuous, naked or half-naked androgynous youth: the literature describes him as womanly or "man-womanish". In its fully developed form, his central cult imagery shows his triumphant, disorderly arrival or return, as if from some place beyond the borders of the known and civilized. His procession
(thiasus)
is made up of wild female followers (maenads) and bearded satyrs with erect penises. Some are armed with the
thyrsus
, some dance or play music. The god himself is drawn in a chariot, usually by exotic beasts such as lions or tigers, and is sometimes attended by a bearded, drunken Silenus. This procession is presumed to be the cult model for the human followers of his Dionysian Mysteries. In his Thracian mysteries, he wears the
bassaris
or fox-skin, symbolizing a new life. Dionysus is represented by city religions as the protector of those who do not belong to conventional society and thus symbolizes everything which is chaotic, dangerous and unexpected, everything which escapes human reason and which can only be attributed to the unforeseeable action of the gods.
Also known as
Bacchus
, the name adopted by the Romans and the frenzy he induces,
bakkheia
. His
thyrsus
is sometimes wound with ivy and dripping with honey. It is a beneficent wand but also a weapon, and can be used to destroy those who oppose his cult and the freedoms he represents. He is also called
Eleutherios
("the liberator"), whose wine, music and ecstatic dance frees his followers from self-conscious fear and care, and subverts the oppressive restraints of the powerful. Those who partake of his mysteries are possessed and empowered by the god himself. His cult is also a "cult of the souls"; his maenads feed the dead through blood-offerings, and he acts as a divine communicant between the living and the dead.
In Greek mythology, he is presented as a son of Zeus and the mortal Semele, thus semi-divine or heroic: and as son of Zeus and Persephone or Demeter, thus both fully divine, part-chthonic and possibly identical with Iacchus of the Eleusinian Mysteries. Some scholars believe that Dionysus is a syncretism of a local Greek nature deity and a more powerful god from Thrace or Phrygia such as Sabazios or Zalmoxis.
Marcianopolis
, or
Marcianople
was an ancient Roman city in Thracia. It was located at the site of modern day Devnya, Bulgaria.
The city was so renamed by Emperor Trajan after his sister Ulpia Marciana, and was previously known as Parthenopolis. Romans repulsed a Gothic attack to this town in 267 (or 268), during the reign of Gallienus. Diocletian made it the capital of the Moesia Secunda province.
Valens made it his winter quarters in 368 and succeeding years, Emperor Justinian I restored and fortified it. In 587, it was sacked by the king of the Avars but at once retaken by the Romans. The Roman army quartered there in 596 before crossing the Danube to assault the Avars.
Between 893 and 972 it was one of the most important medieval cities in south-eastern Europe.
Julia Maesa
- Augusta 218-224/225 A.D.
| Sister of
Julia Domna
| Sister-in-law of
Septimius Severus
| Mother of
Julia Soaemias
and
Julia Mamaea
| Grandmother of
Elagabalus
and
Severus Alexander
| Aunt of
Caracalla
and
Geta
|
Julia Maesa
(7 May ca. 165 AD-ca. 3 August 224) was a Roman citizen and daughter of Julius Bassianus, priest of the sun god Heliogabalus, the patron god of Emesa (modern Homs) in the Roman province of Syria. Grandmother of both the Roman emperors Elagabalus and Alexander Severus, she figured prominently in the ascension of each to the title at the age of fourteen.
Like her younger sister Julia Domna, she was among the most important women to exercise power behind the throne in the Roman empire.
Julia Maesa was married to Syrian noble Julius Avitus and had two daughters Julia Soaemias and Julia Avita Mamaea each one mother of an emperor. Following the accession to the throne of her brother in law Septimius Severus, Julia Maesa moved to Rome to live with her sister. After the murder of her nephew, the emperor Caracalla, and the suicide of Julia Domna, she was compelled to return to Syria. But the new emperor Macrinus did not proscribe her and allowed her to keep her money.
Once back in Syria and possessed of ample funds, Maesa engaged in a plot to overthrow Macrinus and place one of her grandsons, Elagabalus son of Julia Soaemias, in his place. In order to legitimise this pretension, mother and daughter fomented the rumor that the 14 year old boy was Caracalla's illegitimate son. The two Julias were successful, mainly due to the fact that Macrinus was of an obscure origin without the proper political connections, and Elagabalus became emperor.
For her loyalty and support, Elagabalus honored Julia Maesa with the title
Augusta avia Augusti
(Augusta, grandmother of Augustus). When the teenager proved to be a disaster as emperor scorning Roman values with both religious and sexual scandals (even taking the liberty of marrying a Vestal virgin among a rumored five wives during his brief four years reign), Julia Maesa decided to promote instead her fourteen year-old grandson Alexander Severus.
She convinced Elagabalus to adopt Alexander as his heir and he was murdered shortly afterwards by the praetorian guard alongside his mother, both being thrown into the Tiber river in contempt after being dragged from the palace and through the streets, when a rumor circulated that Alexander had died.
Julia Maesa died in an uncertain date around 226 and like her sister Domna before her, was deified.
Elagabalus
-
Emperor
: 218-222 A.D.
Son of
Julia Soaemias
| Husband of
Julia Paula
,
Aquilia Severa
and
Annia Faustina
| Grandson of
Julia Maesa
| Nephew of
Julia Mamaea
| Cousin of
Severus Alexander
| Second-cousin of
Geta
and
Caracalla
(Supposedly a natural son of Caracalla) | Great-nephew of
Septimius Severus
and
Julia Domna
|
Elagabalus
(Marcus Aurelius Antoninus Augustus, ca. 203 - 11 March 222), also known as
Heliogabalus
, was Roman Emperor from 218 to 222. A member of the Severan Dynasty, he was Syrian on his mother's side, the son of Julia Soaemias and Sextus Varius Marcellus. In his early youth he served as a priest of the god Elagabal (in Latin,
Elagabalus
) in the hometown of his mother's family, Emesa. As a private citizen, he was probably named Sextus Varius Avitus Bassianus. Upon becoming emperor he took the name Marcus Aurelius Antoninus Augustus. He was called Elagabalus only after his death.
In 217, the emperor Caracalla was assassinated and replaced by his Praetorian prefect, Marcus Opellius Macrinus. Caracalla's maternal aunt, Julia Maesa, successfully instigated a revolt among the Third Legion to have her eldest grandson (and Caracalla's cousin), Elagabalus, declared emperor in his place. Macrinus was defeated on 8 June 218, at the Battle of Antioch. Elagabalus, barely fourteen years old, became emperor, initiating a reign remembered mainly for sexual scandal and religious controversy.
Later historians suggest Elagabalus showed a disregard for Roman religious traditions and sexual taboos. He replaced the traditional head of the Roman pantheon, Jupiter, with the deity of whom he was high priest, Elagabal. He forced leading members of Rome's government to participate in religious rites celebrating this deity, over which he personally presided. Elagabalus was married as many as five times, lavished favors on male courtiers popularly thought to have been his lovers, employed a prototype of whoopee cushions at dinner parties, and was reported to have prostituted himself in the imperial palace. His behavior estranged the Praetorian Guard, the Senate, and the common people alike.
Amidst growing opposition, Elagabalus, just 18 years old, was assassinated and replaced by his cousin Alexander Severus on 11 March 222, in a plot formulated by his grandmother, Julia Maesa, and carried out by disaffected members of the Praetorian Guard.
Elagabalus developed a reputation among his contemporaries for extreme eccentricity, decadence and zealotry. This tradition has persisted, and in writers of the early modern age he suffers one of the worst reputations among Roman emperors. Edward Gibbon, for example, wrote that Elagabalus "abandoned himself to the grossest pleasures and ungoverned fury." According to B.G. Niebuhr, "The name Elagabalus is branded in history above all others" because of his "unspeakably disgusting life."
Family and priesthood
Elagabalus was born around the year 203 to Sextus Varius Marcellus and Julia Soaemias Bassiana. His father was initially a member of the equestrian class, but was later elevated to the rank of senator. His grandmother Julia Maesa was the widow of the Consul Gaius Julius Avitus Alexianus, the sister of Julia Domna, and the sister-in-law of the emperor Septimius Severus.
His mother, Julia Soaemias, was a cousin of the Roman emperor Caracalla. Other relatives included his aunt Julia Avita Mamaea and uncle Marcus Julius Gessius Marcianus, and their son Alexander Severus. Elagabalus's family held hereditary rights to the priesthood of the sun god Elagabal, of whom Elagabalus was the high priest at Emesa (modern Homs) in Syria.
The deity Elagabalus was initially venerated at Emesa. This form of the god's name is a Latinized version of the Syrian
Ilāh hag-Gabal
, which derives from Ilāh ("god") and
gabal
("mountain" (compare Hebrew: גבל
gə
b
ul
and Arabic: جبل
jabal
)), resulting in "the God of the Mountain" the Emesene manifestation of the deity. The cult of the deity spread to other parts of the Roman Empire in the 2nd century; a dedication has been found as far away as Woerden (Netherlands). The god was later imported and assimilated with the Roman sun god known as Sol Indiges in republican times and as Sol Invictus during the 2nd and 3rd centuries CE. In Greek the sun god is Helios, hence "Heliogabalus", a variant of "Elagabalus".
Rise to power
When the emperor Macrinus came to power, Elagabalus' mother suppressed the threat against his reign by the family of his assassinated predecessor, Caracalla, by exiling them-Julia Maesa, her two daughters, and her eldest grandson Elagabalus-to their estate at Emesa in Syria. Almost upon arrival in Syria she began a plot, with her advisor and Elagabalus' tutor Gannys, to overthrow Macrinus and elevate the fourteen-year-old Elagabalus to the imperial throne.
His mother publicly declared that he was the illegitimate son of Caracalla, therefore due the loyalties of Roman soldiers and senators who had sworn allegiance to Caracalla. After Julia Maesa displayed her wealth to the Third Legion at Raphana they swore allegiance to Elagabalus. At sunrise on 16 May 218, Publius Valerius Comazon Eutychianus, commander of the legion, declared him emperor. To strengthen his legitimacy through further propaganda, Elagabalus assumed Caracalla's names,
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus
.
In response Macrinus dispatched his Praetorian prefect Ulpius Julianus to the region with a contingent of troops he considered strong enough to crush the rebellion. However, this force soon joined the faction of Elagabalus when, during the battle, they turned on their own commanders. The officers were killed and Julianus' head was sent back to the emperor.
Macrinus now sent letters to the Senate denouncing Elagabalus as the
False Antoninus
and claiming he was insane. Both consuls and other high-ranking members of Rome's leadership condemned Elagabalus, and the Senate subsequently declared war on both Elagabalus and Julia Maesa.
Macrinus and his son, weakened by the desertion of the Second Legion due to bribes and promises circulated by Julia Maesa, were defeated on 8 June 218 at the Battle of Antioch by troops commanded by Gannys. Macrinus fled toward Italy, disguised as a courier, but was later intercepted near Chalcedon and executed in Cappadocia. His son Diadumenianus, sent for safety to the Parthian court, was captured at Zeugma and also put to death.
Elagabalus declared the date of the victory at Antioch to be the beginning of his reign and assumed the imperial titles without prior senatorial approval, which violated tradition but was a common practice among 3rd-century emperors nonetheless. Letters of reconciliation were dispatched to Rome extending amnesty to the Senate and recognizing the laws, while also condemning the administration of Macrinus and his son.
The senators responded by acknowledging Elagabalus as emperor and accepting his claim to be the son of Caracalla. Caracalla and Julia Domna were both deified by the Senate, both Julia Maesa and Julia Soaemias were elevated to the rank of Augustae, and the memory of both Macrinus and Diadumenianus was condemned by the Senate. The former commander of the Third Legion, Comazon, was appointed commander of the Praetorian Guard.
Emperor (218-222)
Elagabalus and his entourage spent the winter of 218 in Bithynia at Nicomedia, where the emperor's religious beliefs first presented themselves as a problem. The contemporary historian Cassius Dio suggests that Gannys was in fact killed by the new emperor because he was forcing Elagabalus to live "temperately and prudently." To help Romans adjust to the idea of having an oriental priest as emperor, Julia Maesa had a painting of Elagabalus in priestly robes sent to Rome and hung over a statue of the goddess Victoria in the Senate House. This placed senators in the awkward position of having to make offerings to Elagabalus whenever they made offerings to Victoria.
The legions were dismayed by his behaviour and quickly came to regret having supported his accession. While Elagabalus was still on his way to Rome, brief revolts broke out by the Fourth Legion at the instigation of Gellius Maximus, and by the Third Legion, which itself had been responsible for the elevation of Elagabalus to the throne, under the command of Senator Verus. The rebellion was quickly put down, and the Third Legion disbanded.
When the entourage reached Rome in the autumn of 219, Comazon and other allies of Julia Maesa and Elagabalus were given powerful and lucrative positions, to the outrage of many senators who did not consider them worthy of such privileges. After his tenure as Praetorian prefect, Comazon would serve as the city prefect of Rome three times, and as consul twice. Elagabalus soon devalued the Roman currency. He decreased the silver purity of the
denarius
from 58% to 46.5% - the actual silver weight dropping from 1.82 grams to 1.41 grams. He also demonetized the
antoninianus
during this period in Rome.
Elagabalus tried to have his presumed lover, the charioteer Hierocles, declared Caesar, while another alleged lover, the athlete Aurelius Zoticus, was appointed to the non-administrative but influential position of Master of the Chamber, or
Cubicularius
. His offer of amnesty for the Roman upper class was largely honored, though the jurist Ulpian was exiled.
The relationships between Julia Maesa, Julia Soaemias, and Elagabalus were strong at first. His mother and grandmother became the first women to be allowed into the Senate, and both received senatorial titles: Soaemias the established title of
Clarissima,
and Maesa the more unorthodox
Mater Castrorum et Senatus
("Mother of the army camp and of the Senate"). While Julia Maesa tried to position herself as the power behind the throne and thus the most powerful woman in the world, Elagabalus would prove to be highly independent, set in his ways, and impossible to control.
Religious controversy
Since the reign of Septimius Severus, sun worship had increased throughout the Empire. Elagabalus saw this as an opportunity to install Elagabal as the chief deity of the Roman pantheon. The god was renamed
Deus Sol Invictus
, meaning
God the Undefeated Sun
, and honored above Jupiter.
As a token of respect for Roman religion, however, Elagabalus joined either Astarte, Minerva, Urania, or some combination of the three to Elagabal as wife. Before constructing a temple in dedication to Elagabal, Elagabalus placed the meteorite of Elagabal next to the throne of Jupiter at the temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus.
He caused further discontent when he himself married the Vestal Virgin Aquilia Severa, claiming the marriage would produce "godlike children". This was a flagrant breach of Roman law and tradition, which held that any Vestal found to have engaged in sexual intercourse was to be buried alive.
A lavish temple called the Elagabalium was built on the east face of the Palatine Hill to house Elagabal, who was represented by a black conical meteorite from Emesa. Herodian wrote "this stone is worshipped as though it were sent from heaven; on it there are some small projecting pieces and markings that are pointed out, which the people would like to believe are a rough picture of the sun, because this is how they see them".
In order to become the high priest of his new religion, Elagabalus had himself circumcised. He forced senators to watch while he danced around the altar of Deus Sol Invictus to the accompaniment of drums and cymbals. Each summer solstice he held a festival dedicated to the god, which became popular with the masses because of the free food distributed on such occasions. During this festival, Elagabalus placed the Emesa stone on a chariot adorned with gold and jewels, which he paraded through the city:
A six horse chariot carried the divinity, the horses huge and flawlessly white, with expensive gold fittings and rich ornaments. No one held the reins, and no one rode in the chariot; the vehicle was escorted as if the god himself were the charioteer. Elagabalus ran backward in front of the chariot, facing the god and holding the horses' reins. He made the whole journey in this reverse fashion, looking up into the face of his god.
The most sacred relics from the Roman religion were transferred from their respective shrines to the Elagabalium, including the emblem of the Great Mother, the fire of Vesta, the Shields of the Salii and the Palladium, so that no other god could be worshipped except in company with Elagabal.
Sex/gender controversy
The marriage caused a public outrage because Aquilia was a Vestal Virgin, sworn by Roman law to celibacy for 30 years.
Elagabalus' sexual orientation and gender identity are the subject of much debate. Elagabalus married and divorced five women, three of whom are known. His first wife was Julia Cornelia Paula; the second was the Vestal Virgin Julia Aquilia Severa.
Within a year, he abandoned her and married Annia Aurelia Faustina, a descendant of Marcus Aurelius and the widow of a man recently executed by Elagabalus. He had returned to his second wife Severa by the end of the year. According to Cassius Dio, his most stable relationship seems to have been with his chariot driver, a blond slave from Caria named Hierocles, whom he referred to as his husband.
The
Augustan History
claims that he also married a man named Zoticus, an athlete from Smyrna, in a public ceremony at Rome. Cassius Dio reported that Elagabalus would paint his eyes, epilate his hair and wear wigs before prostituting himself in taverns, brothels, and even in the imperial palace:
Finally, he set aside a room in the palace and there committed his indecencies, always standing nude at the door of the room, as the harlots do, and shaking the curtain which hung from gold rings, while in a soft and melting voice he solicited the passers-by. There were, of course, men who had been specially instructed to play their part. For, as in other matters, so in this business, too, he had numerous agents who sought out those who could best please him by their foulness. He would collect money from his patrons and give himself airs over his gains; he would also dispute with his associates in this shameful occupation, claiming that he had more lovers than they and took in more money.
Herodian commented that Elagabalus enhanced his natural good looks by the regular application of cosmetics. He was described as having been "delighted to be called the mistress, the wife, the queen of Hierocles" and was reported to have offered vast sums of money to any physician who could equip him with female genitalia. Elagabalus has been characterized by some modern writers as transgender, perhaps transsexual.
Fall from power
By 221 Elagabalus' eccentricities, particularly his relationship with Hierocles, increasingly provoked the soldiers of the Praetorian Guard. When Elagabalus' grandmother Julia Maesa perceived that popular support for the emperor was waning, she decided that he and his mother, who had encouraged his religious practices, had to be replaced. As alternatives, she turned to her other daughter, Julia Avita Mamaea, and her daughter's son, the thirteen-year-old Severus Alexander.
Prevailing on Elagabalus, she arranged that he appoint his cousin Alexander as his heir and be given the title of
Caesar
. Alexander shared the consulship with the emperor that year. However, Elagabalus reconsidered this arrangement when he began to suspect that the Praetorian Guard preferred his cousin above himself.
Following the failure of various attempts on Alexander's life, Elagabalus stripped his cousin of his titles, revoked his consulship, and circulated the news that Alexander was near death, in order to see how the Praetorians would react. A riot ensued, and the guard demanded to see Elagabalus and Alexander in the Praetorian camp.
Assassination
The emperor complied and on 11 March 222 he publicly presented his cousin along with his own mother, Julia Soaemias. On their arrival the soldiers started cheering Alexander while ignoring Elagabalus, who ordered the summary arrest and execution of anyone who had taken part in this display of insubordination. In response, members of the Praetorian Guard attacked Elagabalus and his mother:
So he made an attempt to flee, and would have got away somewhere by being placed in a chest, had he not been discovered and slain, at the age of 18. His mother, who embraced him and clung tightly to him, perished with him; their heads were cut off and their bodies, after being stripped naked, were first dragged all over the city, then the mother's body was cast aside somewhere or other while his was thrown into the [Tiber].
Following his assassination, many associates of Elagabalus were killed or deposed, including Hierocles and Comazon. His religious edicts were reversed and the stone of Elagabal was sent back to Emesa. Women were again barred from attending meetings of the Senate. The practice of
damnatio memoriae
-erasing from the public record a disgraced personage formerly of note-was systematically applied in his case.
Frequently Asked Questions
Mr. Ilya Zlobin
, world-renowned expert numismatist, enthusiast, author and dealer in authentic ancient Greek, ancient Roman, ancient Byzantine, world coins & more.
Who am I dealing with?
You are dealing with Ilya Zlobin, ancient coin expert, enthusiast, author and dealer with an online store having a selection of over 15,000 items with great positive feedback from verified buyers and over 10 years experience dealing with over 57,000 ancient and world coins and artifacts. Ilya Zlobin is an independent individual who has a passion for coin collecting, research and understanding the importance of the historical context and significance all coins and objects represent. Most others are only concerned with selling you, Ilya Zlobin is most interested in educating you on the subject, and providing the largest selection, most professional presentation and service for the best long-term value for collectors worldwide creating returning patrons sharing in the passion of ancient and world coin collecting for a lifetime.
How long until my order is shipped?
Orders are shipped by the next business day (after receipt of payment) most of the time.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date could be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date. Any tracking number would be found under your 'Purchase history' tab.
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S. International shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country.
Standard international mail to many countries
does not
include a tracking number, and can also be slow sometimes.
For a tracking number and signature confirmation, you may want to do Express Mail International Shipping, which costs more, however, is the fastest and most secure. Additionally you may be able to receive your order in as little as 3-5 business days using this method. For Express Mail International, it may be possible to place up to 10-15 items in one package (for the one shipping cost) as it is flat rate envelope, which may be the most cost-effective, secure and fastest way to receive items internationally. Send me a message about this and I can update your invoice should you want this method.
Getting your order to you, quickly and securely is a top priority and is taken seriously here.
Great care is taken in packaging and mailing every item securely and quickly.
Please be aware, I cannot take responsibility for any postal service delivery delays, especially for international packages as it may happen in rare instances.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 57,000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be very happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing. Additionally, the coin is inside it's own protective coin flip (holder), with a 2x2 inch description of the coin matching the individual number on the COA.
On the free-market such a presentation alone, can be considered a - value all in itself, and it comes standard with your purchases from me,
FREE.
With every purchase, you are leveraging my many years of experience to get a more complete context and understanding of the piece of history you are getting. Whether your goal is to collect or give the item as a gift, coins presented like this could be more prized and valued higher than items that were not given such care and attention to.
Buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive feedback. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens sometimes that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for their order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.
How and where do I learn more about collecting ancient coins?
Visit the
"Guide on How to Use My Store"
for on an overview about using my store, with additional information and links to all other parts of my store which may include educational information on topics you are looking for.